Traditionally dominated by physical stores, weekend hobbyists, and home improvement enthusiasts, the DIY sector has long been a cornerstone of consumer culture. It has thrived on the human instinct to create, improve, and personalise our surroundings. From building furniture to crafting unique home decor, the DIY sector has always been about the tangible, the tactile, and the hands-on experience.
However, we stand on the precipice of a new era. In an era where the physical and digital worlds are converging, technology is reshaping industries, and the DIY sector is no exception. Welcome to the age of DIY 4.0. This concept represents the digital transformation of the DIY sector, integrating cutting-edge technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), Augmented Reality (AR), and 3D printing into the DIY experience. It’s about bringing the DIY ethos into the 21st century, blending the traditional hands-on approach with the convenience and possibilities of the digital world.
In this digital age, the importance of embracing DIY 4.0 cannot be overstated. As consumer behaviour shifts towards online shopping and e-commerce, and digital natives become a more significant part of the consumer base, the DIY sector must adapt or risk being left behind. DIY 4.0 is not just about survival, though. It’s about harnessing the power of technology to enhance the DIY experience to make it more accessible, convenient, and exciting than ever before. It’s about redefining DIY and opening new horizons for creativity and innovation.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the world of DIY 4.0, exploring its impact on the DIY market, its adoption in the EU and Germany, and how DIY stores can navigate this digital transformation. So, let’s roll up our sleeves and start this exciting journey into the future of DIY.
Adapting and Thriving Amid Global Challenges
The DIY sector has proven flexible and adaptable despite inflationary effects and tense consumer sentiment. It remains the preferred contact for all matters relating to houses, homes and gardens, especially during the pandemic and the current geopolitical situation marked by the Russian attack on Ukraine.
The core assortments of DIY stores have adapted to the changing world situation. People’s focus has shifted from beautification and upgrades to insulation measures, small renovations and complementary heating solutions.
The industry has also ensured supply and product diversity security, which professionals from the craft sector and small businesses particularly appreciate.
Rising prices for building materials, land, and future interest charges have led many people to consider renovations instead of new buildings. Sustainability also plays a role here, as renovations are often more climate-friendly than new buildings.
The industry is responding to rising energy prices by offering products that reduce energy consumption, such as smart products to control LED lighting systems and thermostats. In addition, the industry will continue on the path to sustainability and push it with appropriate transparency.
DIY stores offer a wide range of products and solutions for all areas of life, from building elements for your home office to storage solutions, raised beds or luxurious barbecue kitchens. They are, therefore, a one-stop shop for all needs around the home.
The Evolution of DIY: From Traditional to Digital

The Do-It-Yourself sector has been associated with consumers since at least 1912, primarily in home improvement and maintenance activities. The phrase “do it yourself” became common in the 1950s about the emergence of people undertaking home improvement and various other small craft and construction projects as both creative-recreational and cost-saving activities.
This traditional DIY approach, often called DIY 2.0, was characterised by individuals using raw and semi-raw materials and parts to produce, transform, or reconstruct material possessions. However, with the advent of the digital age, the DIY sector began to transition towards DIY 3.0, which saw the integration of digital tools and online resources into the DIY process. Websites, blogs, and online forums became popular platforms for sharing DIY ideas, techniques, and projects. DIY e-commerce sites emerged, providing a vast array of materials and tools at the click of a button.
The latest evolution in this journey is DIY 4.0, which represents the digital transformation of the DIY sector. This new era is characterised by the integration of advanced technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), Augmented Reality (AR), and 3D printing into the DIY experience. These technologies enhance the DIY process and transform the DIY market, opening new possibilities for customisation, personalisation, and innovation.
The implications of DIY 4.0 are far-reaching, with the potential to reshape the DIY sector and redefine the DIY experience in the coming years.
Revolutionising the DIY Experience with Tech
DIY 4.0 represents the latest evolution in the Do-It-Yourself sector, characterised by the integrating of advanced digital technologies into the DIY process. This new era is about more than just using digital tools or shopping for materials online. It’s about leveraging technology to enhance the DIY experience, to make it more accessible, more efficient, and more innovative. It’s about transforming how we approach DIY, from the planning and design stage to creating and sharing our projects.
Digital transformation is the driving force behind DIY 4.0. As the world becomes increasingly digital, consumer expectations are changing. Today’s consumers demand convenience, personalisation, and instant gratification; the DIY sector is no exception. Digital transformation is about meeting these expectations, about using technology to provide a better, more seamless DIY experience. It’s about making DIY more accessible and appealing to a broader audience, including digital natives with little to no experience with traditional DIY.
Several key technologies are driving the DIY 4.0 revolution. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is used to provide personalised recommendations, automate specific tasks, and enhance the design process. The Internet of Things (IoT) enables smarter, more connected DIY tools and equipment. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) provide immersive, interactive experiences, allowing users to visualise their projects differently. And 3D printing is revolutionising the creation process, allowing users to create complex, customised items from the comfort of their homes.
These technologies are crucial in transforming the DIY sector, opening up new possibilities and redefining what DIY can be. We expect to see even more exciting developments in DIY 4.0 as we continue embracing and integrating these technologies.
Transforming Consumer Behaviour and Expectations
![]()
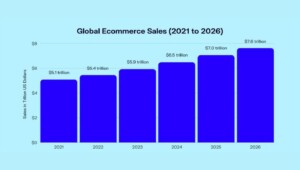
The advent of DIY 4.0 has brought about significant changes in the DIY market, particularly in terms of consumer behaviour and expectations. Today’s consumers are more tech-savvy and demand convenience, speed, and personalisation in their shopping experiences. This has led to a significant shift towards online shopping and e-commerce, with retail e-commerce sales amounting to 4.8 trillion Euros worldwide in 2021, a figure forecasted to grow by 56 per cent over the following years, reaching about 7.7 trillion dollars by 2026.
Mobile apps and social media platforms have also played a crucial role in the evolution of DIY 4.0. They have made it easier for consumers to access DIY resources and tutorials and provided platforms for DIY enthusiasts to share their projects and ideas with a global audience. This has created a more interactive and community-driven DIY culture, where consumers can learn from each other and collaborate on projects.
However, the rise of DIY 4.0 has also posed challenges for traditional DIY stores. With consumers increasingly turning to online platforms for their DIY needs, these stores have had to adapt to stay relevant. Many have embraced digital transformation, integrating online and offline channels to provide a seamless shopping experience. They have also started offering additional services such as online tutorials, workshops, and personalised product recommendations based on customers’ online behaviour.
The Rise of Digital DIY in the Robust EU Market
The DIY market in the EU is a robust and growing sector. According to a report by Statista, the total sales of DIY products in the EU amounted to approximately €95.67 billion in 2021. Germany is one of the leading countries in this sector, with a gross online revenue of around €5.2 billion in 2022, as per another Statista report. A mix of large multinational chains and smaller, independent stores characterises the market.
Several factors have driven the adoption of DIY 4.0 in the EU. These include the increasing prevalence of smart home technologies, the rise of e-commerce, and the growing demand for personalised, DIY solutions among consumers. Companies like Hornbach and OBI have been at the forefront of this trend, leveraging digital technologies to enhance their product offerings and improve customer experience. For instance, Hornbach has developed an online project platform that provides customers with step-by-step guides for various DIY projects. Similarly, OBI offers multiple digital services, including an online shop and a DIY project website.
The transition to DIY 4.0 has been challenging. One of the main issues has been the need to balance the digital and physical aspects of the DIY experience. While digital technologies offer numerous advantages, many customers still value the tactile experience of browsing in a physical store. Companies like Hornbach and OBI have addressed this issue by adopting an omnichannel approach, which integrates online and offline channels to provide a seamless customer experience.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices
The experience of the DIY industry in the EU and Germany offers several lessons for other sectors. One key takeaway is the importance of customer-centricity. By focusing on the needs and preferences of their customers, companies like Hornbach and OBI have successfully navigated the transition to DIY 4.0. Another lesson is the value of innovation. The DIY industry has shown that companies can survive and thrive in a rapidly changing market environment by embracing new technologies and business models.
Navigating Challenges and Opportunities
Embracing Digital Transformation
The first step towards embracing DIY 4.0 is acknowledging the need for digital transformation. Traditional DIY stores must adapt to the changing landscape by integrating digital technologies. This could involve implementing e-commerce platforms, developing mobile apps, or utilising data analytics to gain insights into consumer behaviour. For instance, Bauhaus, a German DIY giant, has successfully integrated digital solutions into its business model, enhancing its customer experience and operational efficiency.
Integrating New Technologies
DIY 4.0 is driven by various technologies such as AI, IoT, VR, AR, and 3D printing. DIY stores can leverage these technologies to offer innovative solutions to their customers. For example, AI can be used to provide personalised product recommendations. At the same time, VR and AR can offer virtual simulations of home improvement projects, helping customers visualise the result before purchasing.
Enhancing Customer Engagement and Personalisation
In the era of DIY 4.0, customer engagement and personalisation have become more critical than ever. DIY stores can use digital platforms to engage with customers, provide personalised experiences, and build long-term relationships. This could involve offering personalised DIY tips, tutorials, and project ideas based on the customer’s interests and past purchases.
Building Partnerships and Collaborations
In the digital age, partnerships and collaborations can drive innovation and growth. DIY stores can collaborate with tech companies, startups, and other industry players to develop innovative solutions and stay ahead of the competition. For instance, partnerships with tech companies can help DIY stores integrate advanced technologies into their operations, enhancing their product offerings and customer experience.
The advent of DIY 4.0 presents both challenges and opportunities for DIY stores in the EU and Germany. By embracing digital transformation, integrating new technologies, enhancing customer engagement, and building strategic partnerships, DIY stores can navigate the challenges of DIY 4.0 and capitalise on the opportunities it presents.
The Future of Do-It-Yourself

The DIY industry faces challenges exacerbated by diversity and ever-changing market conditions. Customer demands, manufacturer ambitions, competitors outside the sector and entirely new business models pose significant difficulties for DIY markets. The dynamics of these changes are rapidly increasing in the wake of digitalisation.
Eight hypotheses:
- Accessing customers in the digital age is the greatest challenge for established DIY stores. Customers increasingly use digital channels and contact points to inform themselves and purchase. However, established DIY stores play a subordinate role in this area from the customer’s perspective, which means customer access could be lost in the medium term.
- The classic “self-service DIY store” business model is outdated in the age of platforms. In times of digital platforms and seemingly unlimited (price) transparency, the trade margin business is under pressure. DIY stores must develop new business models whose value proposition is not exhausted in the mere supply of products.
- Consistent profiling is the only way out in the heterogeneous market environment. The DIY sector is one of the most complex and heterogeneous sectors of the retail industry due to the extreme breadth and depth of the product range, the diverse target groups and the numerous distribution channels. Given this heterogeneity, DIY stores constantly face new competitors who attack their positioning.
- New forms of cooperation with manufacturers are the basis for the future viability of DIY stores. Changed sales strategies of manufacturers require a rethinking of existing processes and an adjustment of sales structures.
- Small-space formats with service, advice, and experience are the answer to high-shelf labyrinths. Competition within the classic DIY business is becoming increasingly intense. The lack of differentiation between competitors’ formats leads to increased price pressure. The predominant focus of DIY stores on space growth in cut-throat competition is blocking the opportunity to escape unprofitable uniformity with new formats.
- Emerging trends suggest a move towards more personalised and interactive DIY experiences. For instance, AI could provide personalised project recommendations based on users’ past projects and preferences. VR/AR technologies could offer immersive tutorials and simulations, allowing users to virtually ‘try before they buy’ or practice a project before starting it in the real world.
- 3D printing technology is also set to revolutionise the DIY sector. With the ability to create custom parts and tools, DIY enthusiasts will have even more freedom and flexibility in their projects. This could also lead to a rise in DIY micro-businesses, where individuals create and sell their custom-made DIY products.
- Sustainability and eco-friendliness are also expected to play a significant role in the future of DIY. As awareness of environmental issues grows, many DIY enthusiasts seek green materials and sustainable practices for their projects. This could lead to a rise in ‘eco-DIY’, focusing on upcycling, recycling, and using sustainable materials.
In conclusion, the future of DIY 4.0 appears promising, with many thrilling advancements on the horizon. As technology evolves, the DIY sector will follow suit, presenting new opportunities and challenges for DIY stores and enthusiasts. Therefore, the DIY store’s future lies in adapting to digital trends and developing new business models beyond mere product supply. Collaboration with manufacturers and focusing on service, advice, and experience will become increasingly crucial in this evolving landscape.







