The customs tariff number is essential when importing products from a third country and when exporting, where it is used in the corresponding shipping documents. The customs tariff in force in the EU is based on Regulation No. 2658/87 from July 23, 1987, defining the tariff and statistical nomenclature, and on the Common Customs Tariff (CCT), which introduced the Combined Nomenclature (CN) as a universally binding, harmonised tariff and statistical nomenclature.
Each year, a complete version of the CN, together with the applicable tariff rates, is prepared by the European Commission and published in the Official Journal of the EU to ensure the information remains up-to-date.
Common Customs Tariff
The Common Customs Tariff (CCT) applies to the import of goods across the external borders of the EU (so-called third-country imports). The free movement of goods within the Member States has been permitted since the introduction of the internal market. With the Common Customs Tariff, the EU follows the principle that EU-based producers should be able to compete fairly and equally on the internal market with manufacturers exporting from other countries/territories. The tariff is the same for all EU members, but the tariff rates differ depending on the types of imports. As a community of Member States, the EU can also decide on sanctions or embargoes on third-country goods, which gives the community more political and economic power.
The tariff classification of goods
The term “tariff classification of goods” means assigning a good to a tariff heading of the nomenclature. The customs duty and tax rate are determined based on this classification. It is important to note that some goods are duty-reduced or duty-free, depending on the country of origin or type of good.
The customs tariff number can be determined using the “List of Goods for Foreign Trade Statistics”. The list of goods is available from the German Federal Statistical Office (Destatis) online or in book form.
Areas of application of the customs tariff number
The customs tariff number is used when importing products from countries outside EU borders into the EU. However, it also plays a vital role in export, as noted in the respective shipment’s Export Accompanying Documents (EAD).
The customs tariff number may also be used when
- An import or export licence is applied for
- Import or export restrictions are to be checked
- A certificate of origin is to be issued
- An export refund or similar has to be applied for
- One needs to determine whether a product is subject to excise duty
- One wants to ascertain whether a reduced VAT rate applies (if the CN is used as a reference)
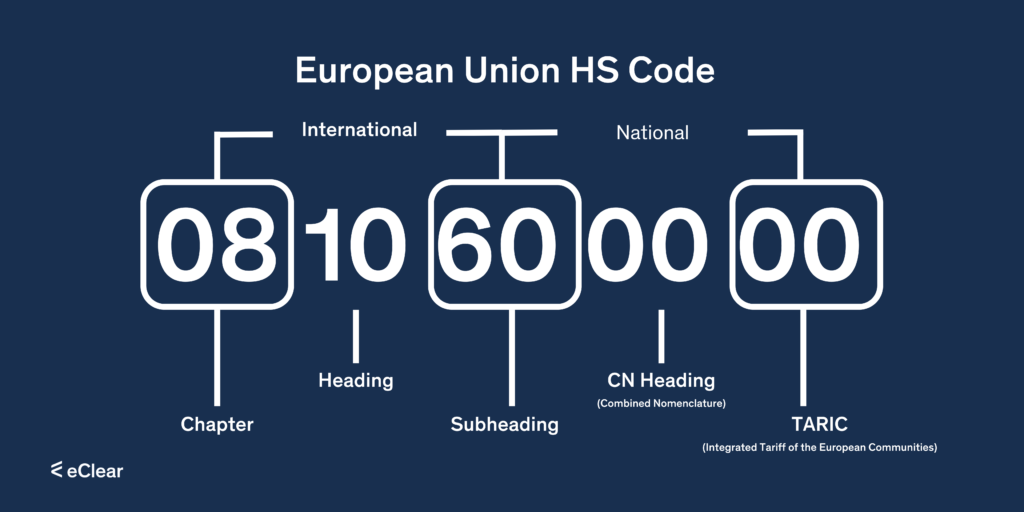
Structure of the customs tariff number
The customs tariff number consists of ten digits. However, each country has an eleven-digit number for national use only.
The EU classification system consists of two elements:
The Combined Nomenclature (CN)
The CN is the 8-digit EU coding system in this 11-digit code number. From this 8-digit EU coding system, the Harmonized System (HS) assigns the first six digits.
The Harmonized System (HS)
The HS is an internationally standardised system of names (designations) and numbers (codes) for classifying commercial goods. In this product nomenclature, each product is assigned a 6-digit code determined by the World Customs Organization (WCO). The HS is a description and coding system designed to provide a uniform classification of goods worldwide. Countries that have adopted the HS are not permitted to change the descriptions of a heading, subheading, or four/six-digit numerical codes.
The Harmonized System is primarily used to set tariffs (import duties), record international trade statistics, establish rules of origin, determine customs compliance, collect government revenues, conduct trade negotiations, or monitor prohibited and restricted goods.
Starting with the six-digit code, the HS code is extended by two digits (position 7 and 8 of the code number) using the Combined Nomenclature (CN) of the European Communities.
Integrated Tariff of the European Union (TARIC)
The TARIC contains information on all trade policies and tariff measures applicable to certain goods in the EU (e.g. temporary suspension of duties, anti-dumping duties).
It is composed of the 8-digit CN code and two additional digits (TARIC subheadings). The ninth and tenth digits encode Community measures such as anti-dumping rules, tariff suspensions or tariff quotas.
The eleventh digit of the code number is for national use only. It is used, for example, to encode VAT rates, national bans, or restrictions. This 11-digit code number must always be shown in an import declaration.
Example assignment of the customs tariff number for an article
Product: Bag For Good, model “Candy”
What is it?
It is a practical shoulder bag.
To which section does it belong?
It belongs to Section 8:
- Raw hides and skins, leather, fur skins and articles thereof
- Saddlery and harness
- Travel goods, handbags and similar containers
- Articles of animal gut (apart from silkworm gut)
To which chapter within Section 8 does the product belong?
It belongs to Article 42:
- Leather goods
- Saddlery and harness
- Travel goods, handbags and similar containers
- Articles of animal gut (apart from silkworm gut)
To which heading within Chapter 42 does the bag belong?
It belongs to 4202: boots, suitcases, vanity cases, attaché cases, briefcases, school satchels, spectacle cases, binocular cases, camera cases, musical instrument cases, gun cases, holsters and similar containers; travelling bags, insulated food or beverage bags, toiletry bags, knapsacks and backpacks, handbags, shopping bags, wallets, purses, map cases, cigarette cases, tobacco pouches, tool bags, sports bags, bottle cases, jewellery boxes, powder cases, cutlery cases and similar containers, of leather or composition leather, of sheeting of plastics, of textile materials, of vulcanized fibre or paperboard, or wholly or mainly covered with such materials or with paper.
To which subheading within heading 4202 does it belong?
It belongs to subheading 420229: handbags, whether with shoulder strap, including those without handle, with outer surface of vulcanized fibre or paperboard or entirely or mainly covered with such materials or paper.
Which subheading within subheading CN is more suitable for our product?
Within this subheading, the subheading is CN 42022900.
eClear TAX Code
The eClear Tax Engine includes 1.2 million tax codes and customs tariffs. It contains 300,000 continuously updated exemption regulations from all EU 27 countries. This globally unique database works with a 14-digit tax code, ensuring a highly detailed assignment of products and their properties with all exemptions.
Let’s stay in touch!
Stay up to date on the latest market trends, best practices and regulatory changes affecting cross-border trade by following us on LinkedIn.








